AI in manufacturing involves using advanced algorithms, machine learning, and data analysis to enhance every stage of the production process. From predictive maintenance that minimizes costly downtime to automated quality checks that ensure defect-free products, AI is making factories smarter, faster, and more efficient. A 2023 report by McKinsey states that 20 percent of EBIT in 2022 are using AI-driven solutions.
This shift isn’t just about machines working harder; it’s about making them work smarter by analyzing vast amounts of data in real time to make decisions that were once impossible without human intervention.
Smarter factories powered by AI enable manufacturers to respond quickly to market changes, meet customer demands, and improve sustainability by reducing energy consumption and waste. A World Economic Forum study from 2024 highlighted that over 65% of leading manufacturers are investing in AI technologies to improve their operations and stay ahead of the competition.
These smarter factories don’t just improve efficiency; they set the foundation for a more innovative, sustainable, and resilient manufacturing future.
What is AI in Manufacturing?
Imagine a factory where machines can predict their own breakdowns, robots work alongside humans seamlessly, and AI production lines optimize themselves to reduce waste and boost efficiency. AI in manufacturing refers to the use of intelligent algorithms, data analysis, and automation to improve every aspect of the production process. By leveraging software development with AI, manufacturers can achieve smarter decision-making, faster production, and higher quality, all while cutting costs. According to a 2024 report by Deloitte, over 70% of manufacturers have begun integrating AI technologies into their operations, transforming the way products are made.
Key AI Technologies Used in Manufacturing
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning enables systems to analyze data, identify patterns, and make predictions. In manufacturing, ML helps optimize production schedules, detect anomalies in machinery, and predict maintenance needs. For example, AI-driven ML systems can analyze sensor data from machines and predict failures before they happen, reducing downtime by up to 50%.
2. Computer Vision
Computer vision uses cameras and AI algorithms to inspect and monitor products in real time. This technology is widely used in quality control to detect defects that human eyes might miss. For example, Tesla uses computer vision to ensure precision in assembling electric vehicles, improving quality and reducing waste.
3. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics combines historical and real-time data to forecast future trends. In manufacturing, this helps optimize supply chains, manage inventory, and predict market demand. AI manufacturing companies using predictive analytics reduced inventory costs and improved delivery times more.
4. Robotics
AI-powered robots are transforming assembly lines. These robots can perform repetitive tasks, collaborate with humans (known as cobots), and adapt to changing AI in production requirements. For instance, BMW uses AI-driven robots for tasks like welding and painting, achieving greater accuracy and efficiency.
Integration with Other Technologies
AI doesn’t work in isolation—it integrates with other technologies to unlock its full potential.
Internet of Things (IoT):
Sensors in IoT devices collect real-time data from machines and processes, which AI analyzes to make informed decisions.One of the AI in manufacturing examples is IoT-enabled factories that use AI to monitor energy consumption and reduce waste.
Cloud Computing:
Cloud platforms provide the computational power needed for AI to process vast amounts of data quickly. This makes it easier for manufacturers to implement AI without investing in costly on-site infrastructure.
Digital Twins:
AI creates virtual replicas of physical assets, allowing manufacturers to simulate and optimize processes before implementing them on the factory floor.
Key AI Applications in Manufacturing
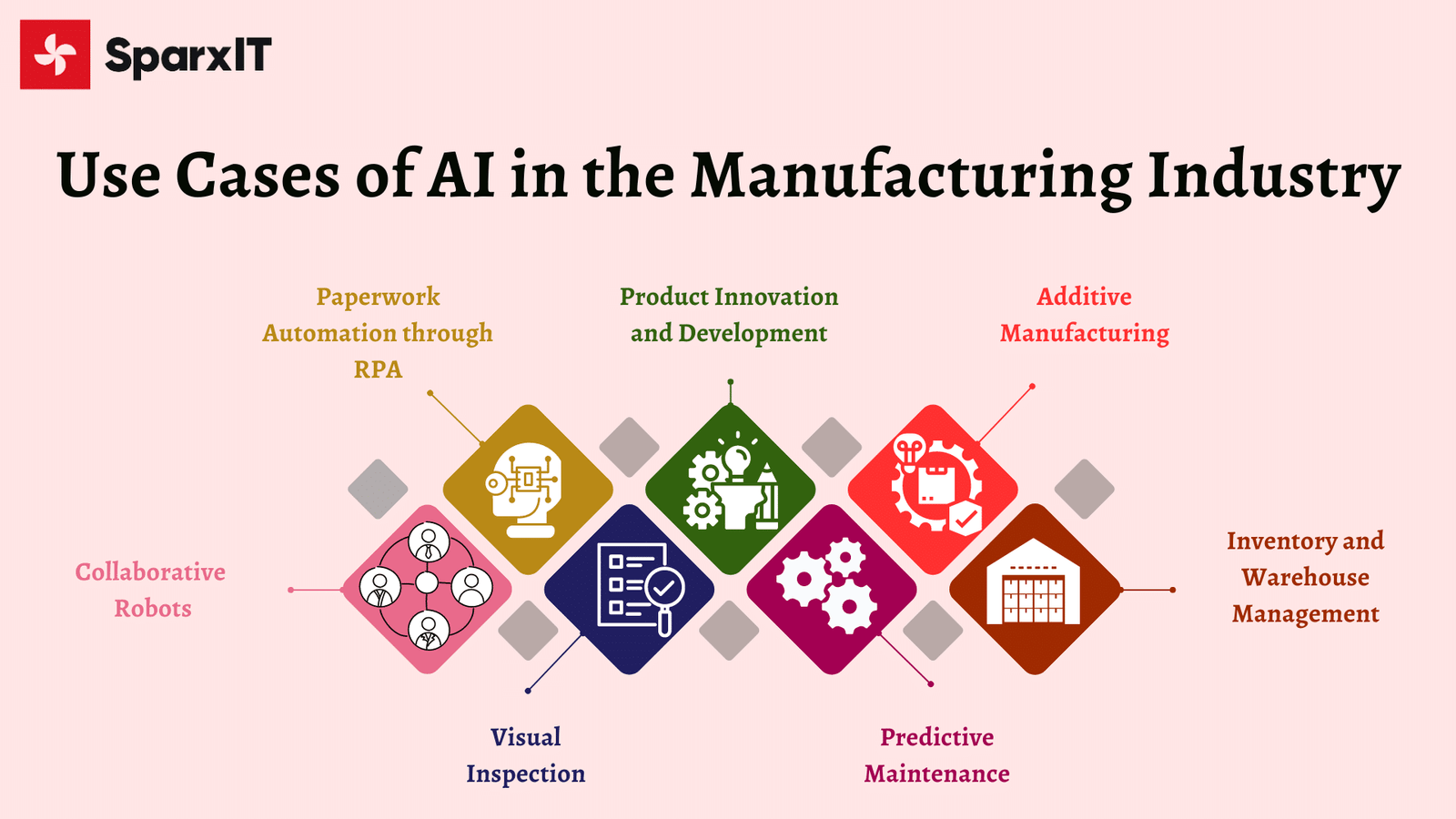
Source: https://www.sparxitsolutions.com/blog/ai-in-manufacturing/
AI is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by making operations smarter, faster, and more efficient. From predicting equipment failures to optimizing energy usage, AI applications are improving productivity while reducing costs. Here’s how AI is transforming manufacturing across various key areas:
1. Predictive Maintenance
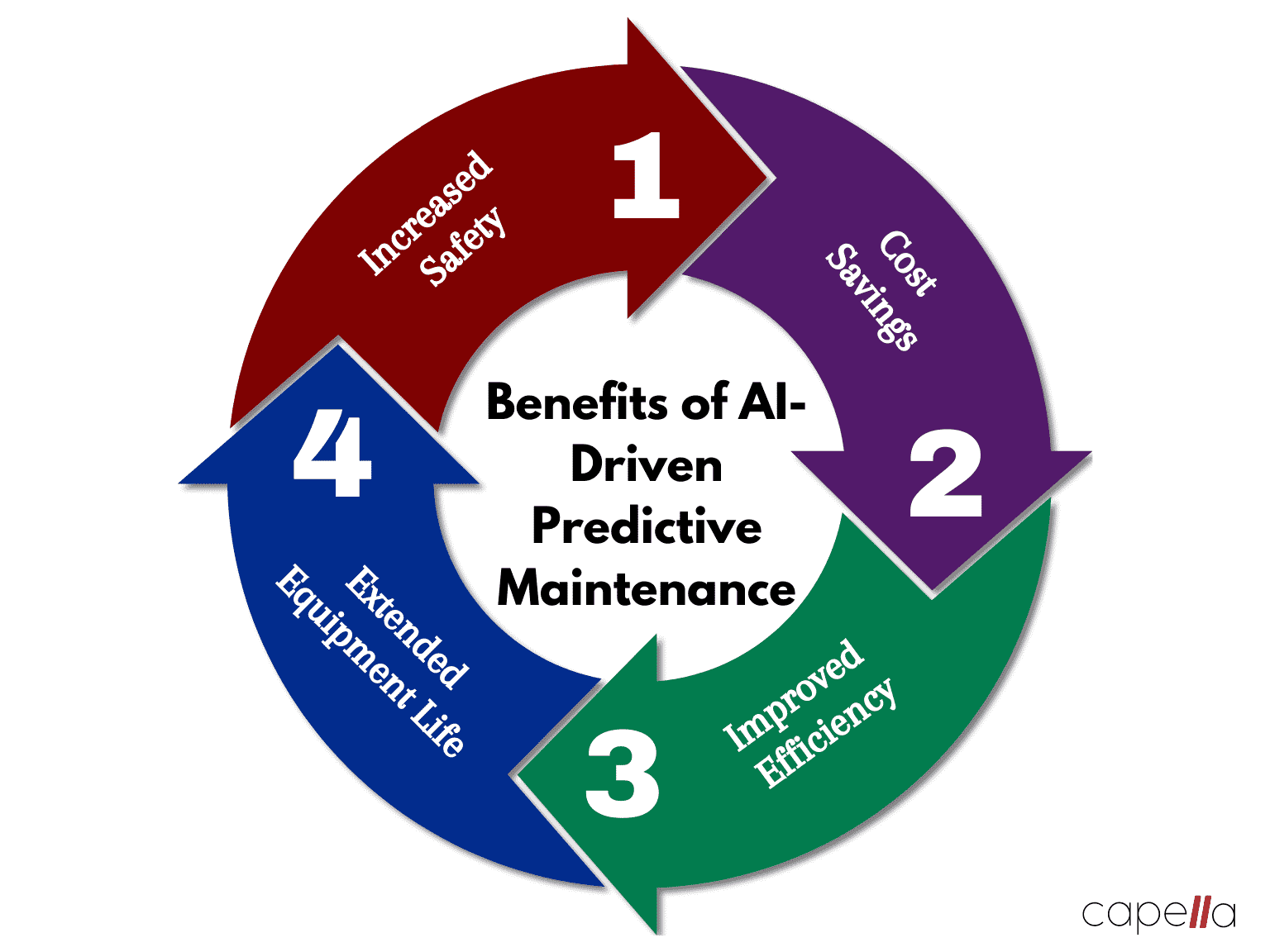
Source: https://www.capellasolutions.com/blog/using-ai-for-predictive-maintenance-in-manufacturing
Unplanned downtime is one of the biggest challenges in manufacturing, costing industries billions every year. AI addresses this issue through predictive maintenance. By analyzing data from sensors installed on machinery, AI can identify potential problems before they lead to equipment failure. For example, IBM Maximo, an AI system can detect unusual vibrations or temperature spikes in a machine, signaling the need for repairs. According to a 2024 report by McKinsey, manufacturers using predictive maintenance have reduced downtime by up to 20% and increase equivalent to more than 500,000 barrels of oil annually.
2. Quality Control and Inspection
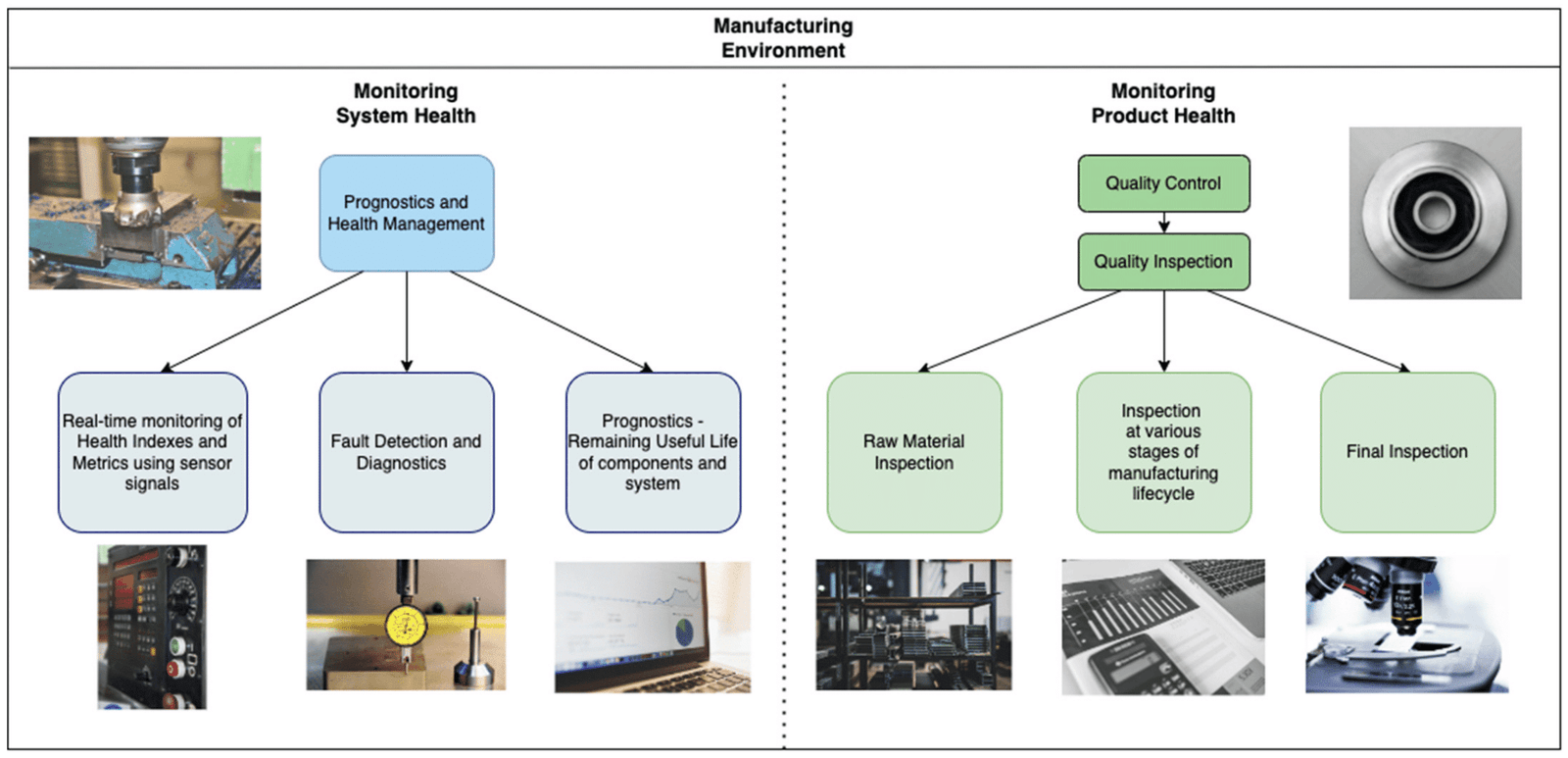
Source: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-666X/14/3/570
Maintaining high product quality is essential for customer satisfaction and brand reputation. AI-powered computer vision systems use cameras and advanced algorithms to detect defects in real time during an AI production system. Unlike human inspectors, these systems can work continuously without fatigue, ensuring consistent quality. For instance, companies like BMW use AI to inspect vehicle components on assembly lines, reducing defects by 30% compared to manual methods.
3. Supply Chain Optimization
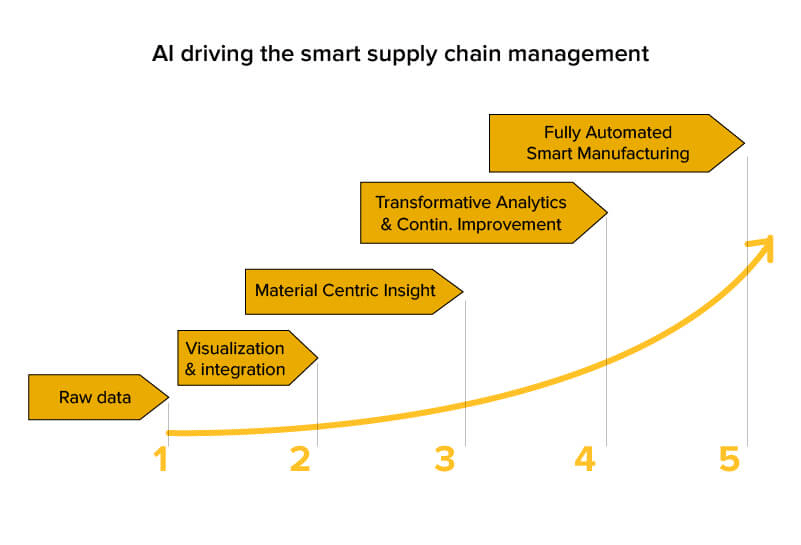
Source: https://appinventiv.com/blog/ai-in-supply-chain-analytics/
AI is a game-changer for managing supply chains, which are often complex and prone to inefficiencies. AI algorithms analyze data to optimize inventory levels, forecast demand, and improve logistics. For example, Aramco AI can predict the needed materials based on historical and real-time data, preventing overstocking or shortages.
4. Production Planning and Scheduling
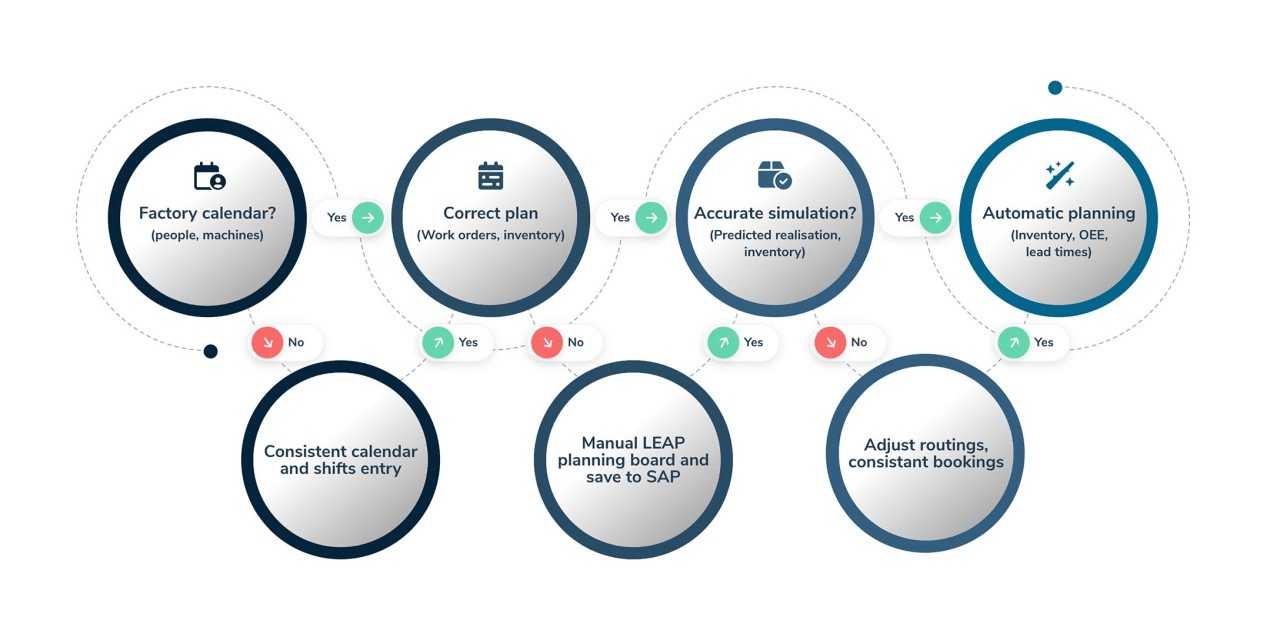
Source: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/four-steps-implementing-ai-production-planning-tomaz-suklje/
Efficient production planning is critical to meeting deadlines and maximizing output. AI helps optimize production schedules by analyzing machine availability, workforce capacity, and demand patterns. This ensures that resources are used effectively while minimizing delays. For example, an artificial intelligence factory producing consumer electronics might prioritize producing high-demand products during peak seasons, boosting profitability.
5. Robotics and Automation
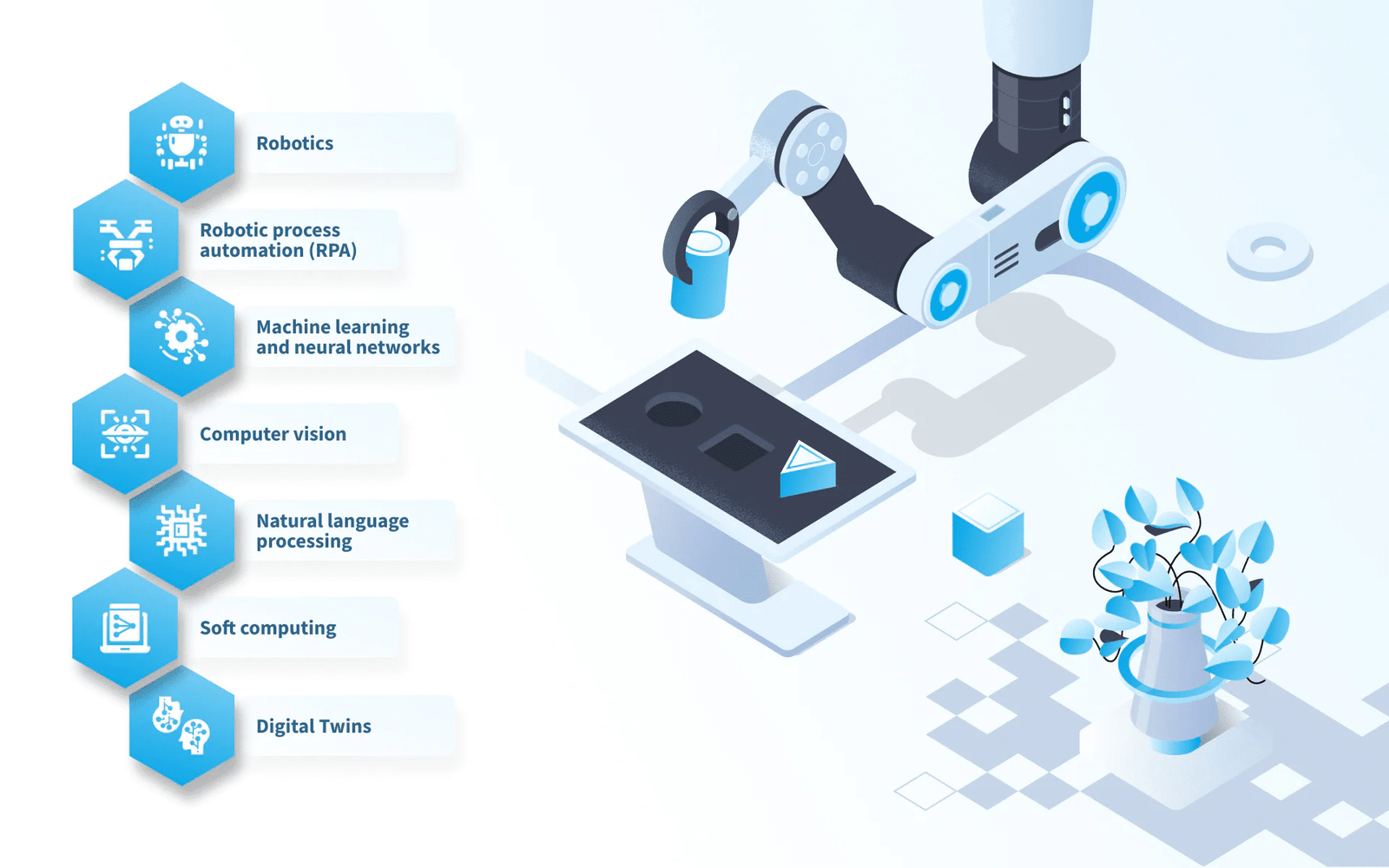
Source: https://nix-united.com/blog/ai-in-manufacturing-between-human-and-robotic-era/
Robots have been used in manufacturing for decades, but AI is taking them to the next level. Autonomous robots powered by AI can perform complex tasks such as assembly, welding, and packaging with high precision. Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside humans to increase productivity. Tesla, for example, uses AI-driven robots extensively in its production lines to assemble electric vehicles, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
6. Energy Optimization
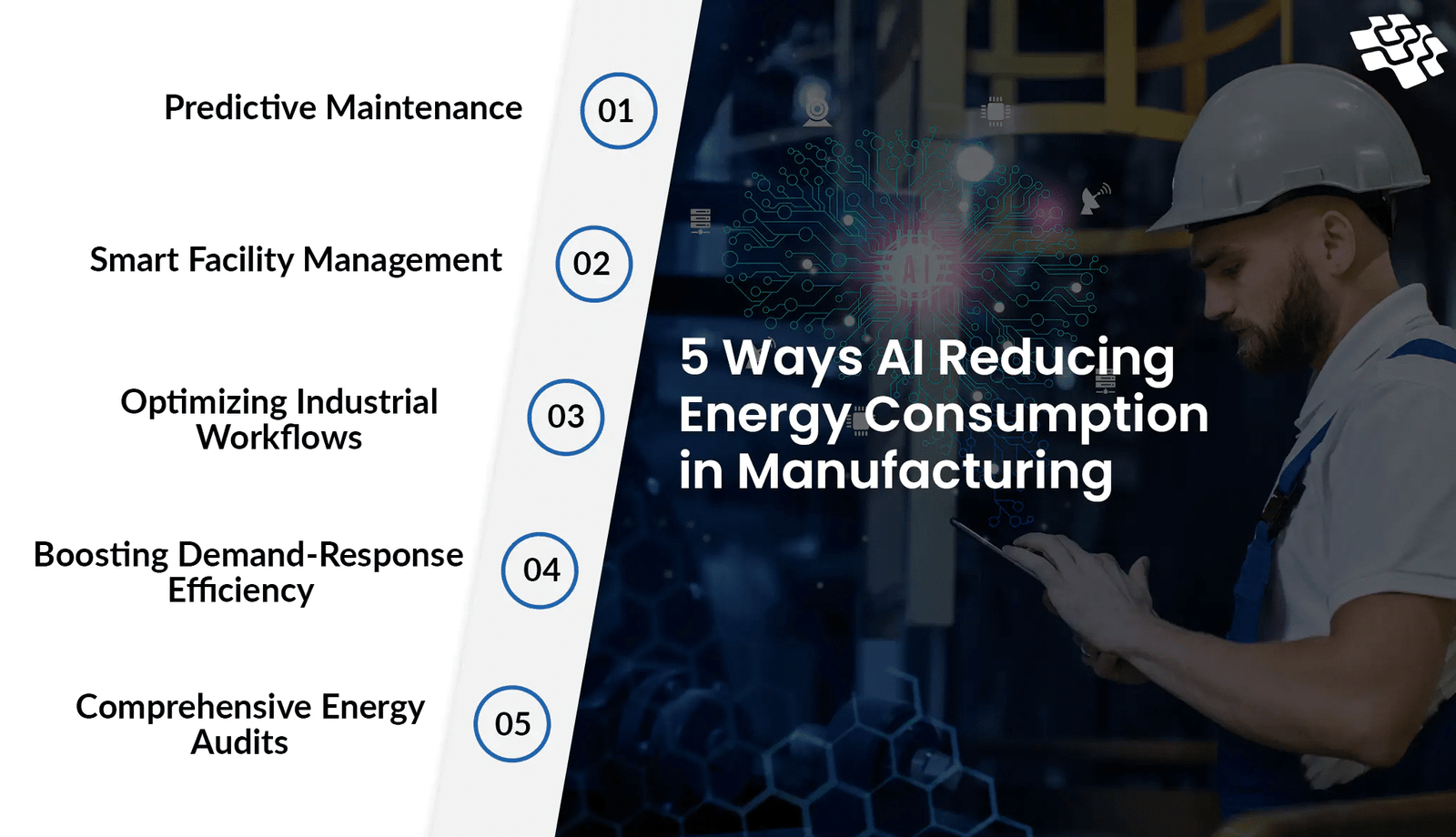
Source: https://nextgeninvent.com/blogs/ai-reducing-energy-consumption-in-manufacturing/
Energy costs are a significant expense in manufacturing, and AI helps reduce these costs through smarter energy management. AI systems monitor energy consumption in real time, identify inefficiencies, and suggest ways to optimize usage. For example, factories can use AI to adjust machine operations during off-peak hours when energy costs are lower. A 2024 study by the International Energy Agency found that 15% incorporated AI for manufacturing companies in production processes.
Top Tools of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing
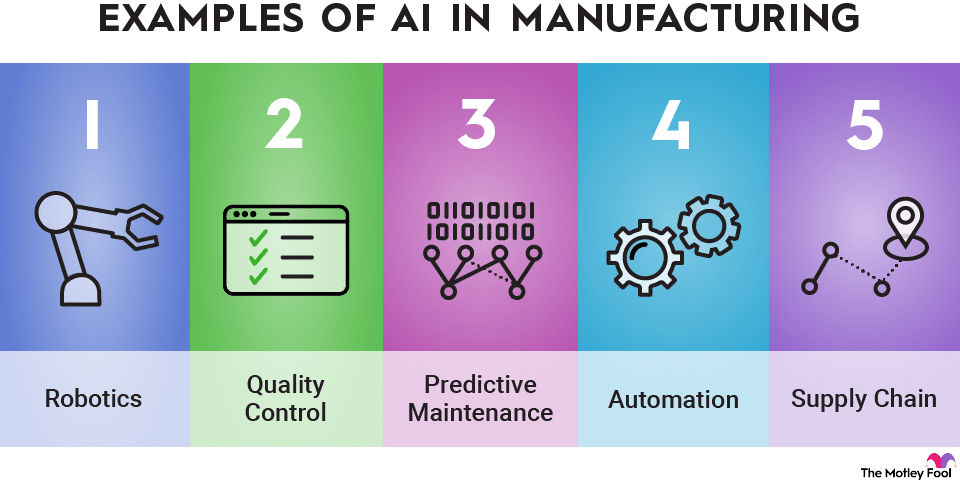
Several AI tools are leading this revolution, helping manufacturers solve problems, improve quality, and reduce costs. Let’s explore the top five tools reshaping the industry:
1. TensorFlow
TensorFlow, developed by Google, is a widely used open-source AI platform. It enables manufacturers to build and deploy machine learning models for tasks such as predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization. TensorFlow excels in handling large datasets, making it ideal for analyzing sensor data from machines. For instance, manufacturers can use TensorFlow to predict equipment failures. The tool’s versatility and scalability make it a favorite among manufacturers of all sizes.
2. IBM Watson
IBM Watson is an AI platform designed for business applications, including manufacturing. It offers tools for predictive analytics, supply chain management, and operational efficiency. IBM Watson’s natural language processing capabilities allow it to interpret unstructured data, such as maintenance logs, to uncover hidden insights.
3. Siemens MindSphere
MindSphere is an industrial IoT (Internet of Things) platform from Siemens that uses AI to monitor and optimize manufacturing operations. It connects machines and systems, collects data, and analyzes it in real time. Manufacturers can use MindSphere to identify bottlenecks, optimize energy usage, and improve machine performance.
4. Microsoft Azure Machine Learning
Microsoft Azure Machine Learning provides a cloud-based platform for creating and managing AI models. It is widely used in manufacturing for tasks like demand forecasting, production planning, and predictive maintenance. Azure’s integration with other Microsoft tools makes it easy to deploy AI solutions at scale.
5. Vuforia
Vuforia, by PTC, is an augmented reality (AR) platform enhanced by AI. It is used in manufacturing for training, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Workers can use Vuforia-powered AR glasses to view real-time instructions or diagnose equipment issues. This reduces errors and accelerates processes.
AI in manufacturing case study: Collaborative Robots (Cobots) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
The integration of collaborative robots (cobots) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are designed to work alongside human employees, enhancing productivity, minimizing errors, and improving overall quality. According to Rockwell Automation’s “9th Annual State of Smart Manufacturing” report, 95% of manufacturers have either invested in or plan to invest in AI and machine learning (ML) for cobots and AMRs in 2024.
Adoption and Impact
Amazon’s Deployment of Robots: Amazon exemplifies the transformative power of cobots and AMRs in manufacturing and logistics. The company has deployed over 750,000 robots in its fulfillment centers, working in tandem with human employees. Among these, the Sequoia robot has been a game-changer. This advanced robotic tool can identify and store inventory up to 75% faster than traditional methods. Sequoia also reduces the time required to process orders by up to 25%, enhancing shipping predictability and enabling more products to qualify for same-day or next-day delivery.
Key Benefits
- Enhanced Workforce Efficiency: Cobots and AMRs complement human efforts by handling repetitive and physically demanding tasks, freeing employees for more complex roles.
- Error Reduction: With precise operations and minimal human intervention, these robots significantly lower the chances of errors in manufacturing and logistics.
- Improved Speed and Quality: Tools like Sequoia demonstrate how automation accelerates workflows and maintains high standards of quality.
Emerging Technologies: Drones in Manufacturing
Beyond cobots and AMRs, drones are gaining traction in the manufacturing sector. Dones are being used for inventory management, inspections, and monitoring, showcasing another frontier of AI-driven innovation in manufacturing.
Benefits of Using AI in Manufacturing
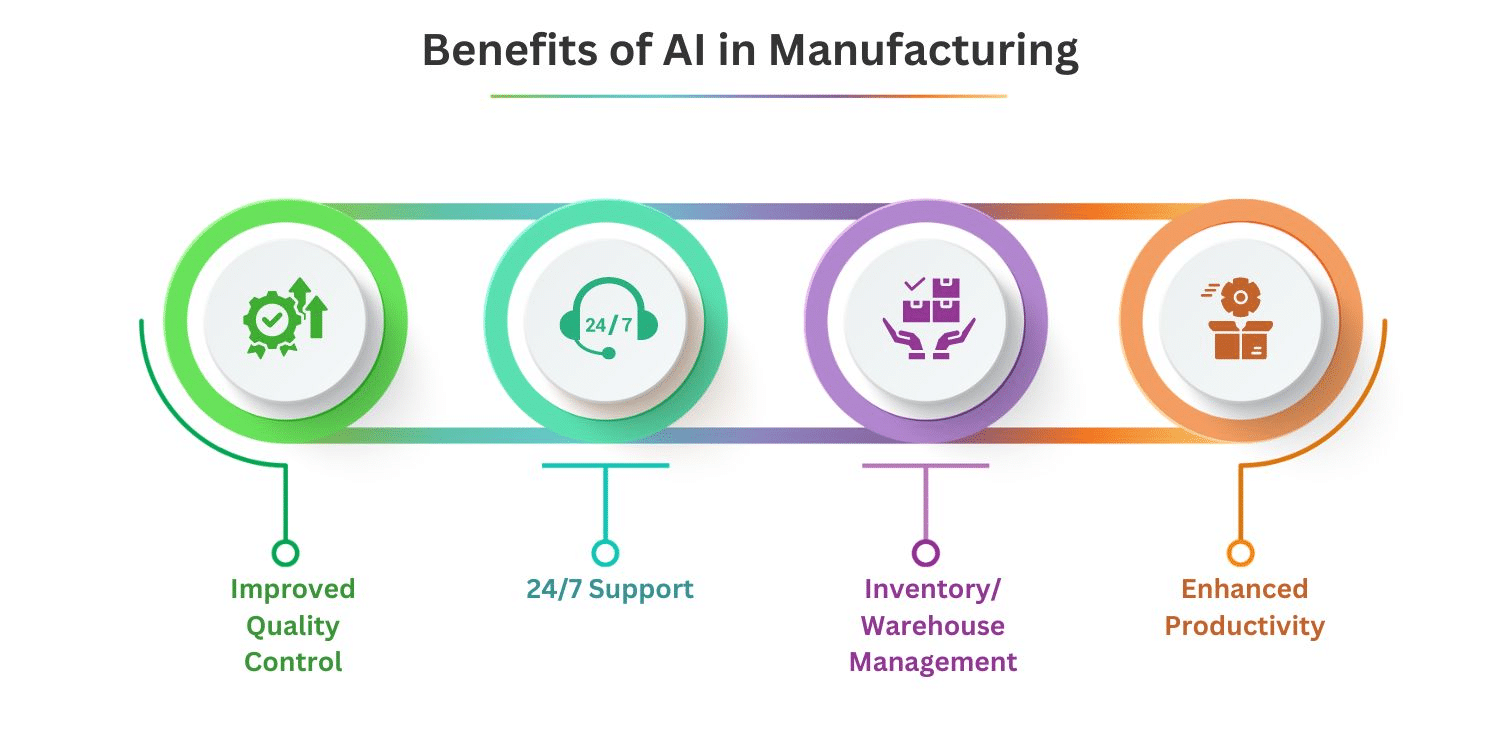
Source: https://aitglobalinc.com/ai-in-manufacturing-industry/
By leveraging AI, manufacturers can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, quality, and adaptability. Here are the key benefits of using AI in semiconductor manufacturing:
1. Improved Efficiency
AI enables faster production cycles while minimizing waste. Smart algorithms analyze data from machines and processes to identify inefficiencies and optimize workflows. For instance, AI-powered predictive maintenance systems monitor equipment in real-time, reducing unplanned downtime. Additionally, manufacturers using AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up workers for higher-value activities and speeding up overall production.
2. Enhanced Product Quality
Consistent quality is crucial in manufacturing, and AI makes this possible. AI tools like computer vision systems detect defects during production in real-time, ensuring only top-quality products reach customers. For example, companies like Siemens use AI to reduce defects in production lines. AI also ensures that quality checks are not affected by human fatigue, leading to more reliable results.
3. Cost Reduction
AI-driven solutions help manufacturers save money in several ways. Predictive maintenance minimizes repair costs by addressing issues before they escalate. Energy optimization systems reduce power consumption, cutting operational expenses. Manufacturers using AI for energy efficiency saved an average of 15% on energy bills. Combined with reduced waste and improved efficiency, these cost savings can significantly boost profitability.
4. Greater Flexibility
Manufacturers today need to respond quickly to changing AI in manufacturing market demands. AI provides the flexibility to adapt production lines for different products or fluctuating order volumes. For example, AI-powered scheduling systems can prioritize high-demand products during peak seasons. This adaptability helps manufacturers meet customer demands without overproducing, reducing both costs and waste.
5. Better Decision-Making
Data is the backbone of smart manufacturing, and AI turns this data into actionable insights. From forecasting demand to optimizing supply chains, AI helps manufacturers make informed decisions. Manufacturers using AI for supply chain optimization saw a 25% improvement in delivery times and reduced logistics costs by 20%. With real-time insights, manufacturers can plan better, allocate resources efficiently, and avoid costly disruptions.
Challenges in Implementing AI in Manufacturing
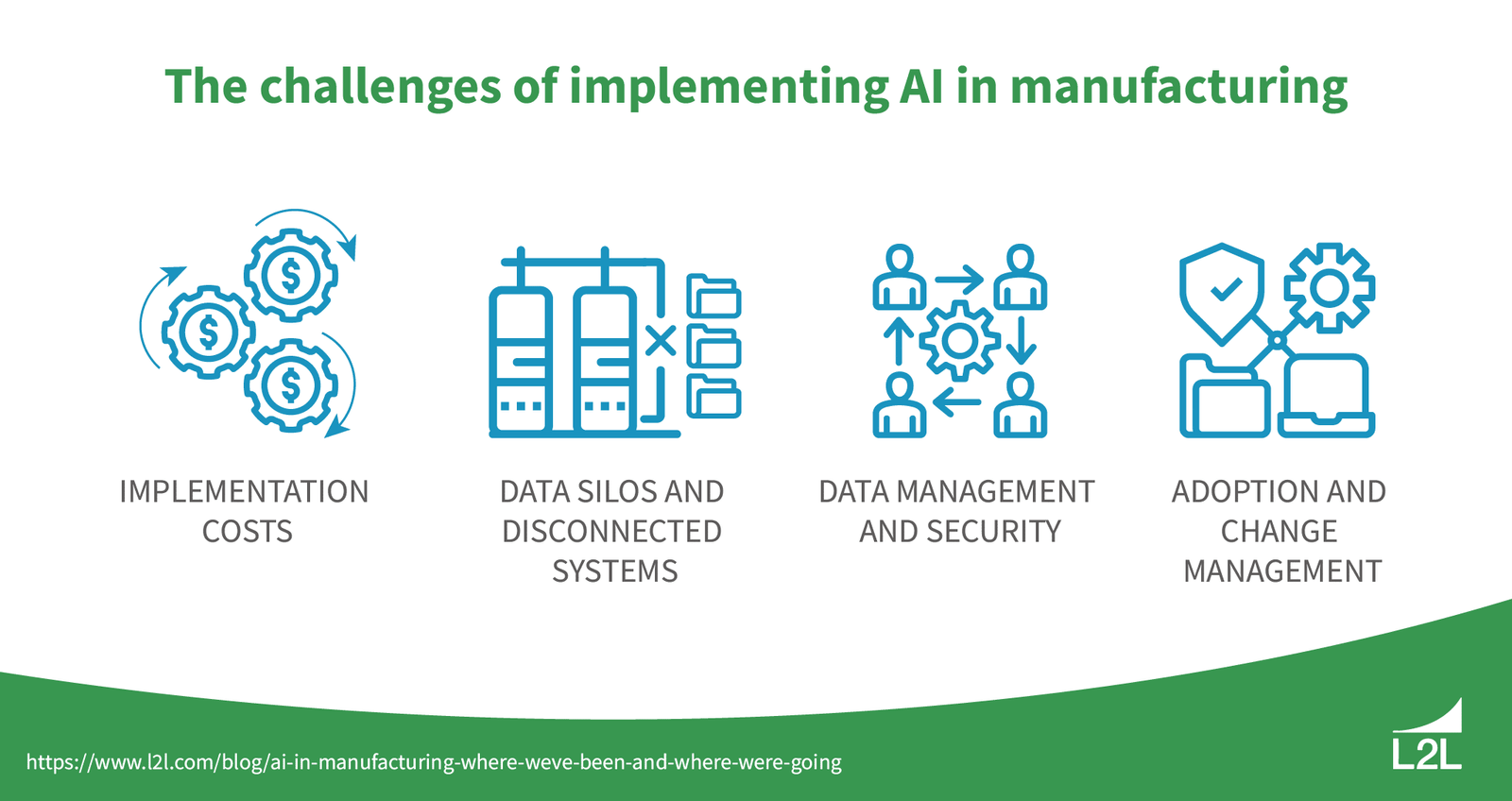
Source: https://www.l2l.com/blog/ai-in-manufacturing-where-weve-been-and-where-were-going
Adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) in manufacturing promises a future of smarter and more efficient operations, but the journey is not without hurdles. While the benefits are clear, manufacturers face several challenges that require careful planning and solutions.
1. High Initial Investment Costs
AI implementation often demands a significant financial commitment. From purchasing advanced hardware and software to training employees, the upfront costs can be daunting, especially for small and medium-sized manufacturers. Setting up an AI-driven manufacturing system could cost anywhere from $500,000 to $5 million, depending on the scale and complexity. Although these investments pay off in the long term, the initial barrier remains a concern for many organizations.
2. Need for Skilled Personnel
AI systems are complex and require skilled professionals to manage them. This includes data scientists, AI engineers, and IT specialists who can develop, deploy, and maintain these systems. However, there is a global shortage of such talent. Manufacturers struggle to find the right expertise to manage AI technologies. Without skilled personnel, even the best AI systems cannot be utilized to their full potential.
3. Integration with Legacy Systems
Most manufacturing facilities rely on legacy systems that were not designed to work with modern AI tools. Integrating AI with these older systems can be technically challenging and time-consuming. For instance, older machinery may lack the sensors needed to collect real-time data, making AI adoption more complicated. Manufacturers see legacy system integration as a major barrier to AI implementation. Upgrading these systems or finding ways to connect them with AI tools requires significant effort and investment.
4. Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Concerns
AI systems thrive on data, but managing large volumes of sensitive information introduces privacy and security risks. Manufacturing data often includes proprietary processes, trade secrets, and customer information, which are prime targets for cyberattacks. Manufacturing sector is the third most targeted industry for cyberattacks, with an average breach costing $4.5 million. Ensuring data privacy and securing AI systems against cyber threats is critical but requires constant vigilance and resources.
Future of AI in Manufacturing
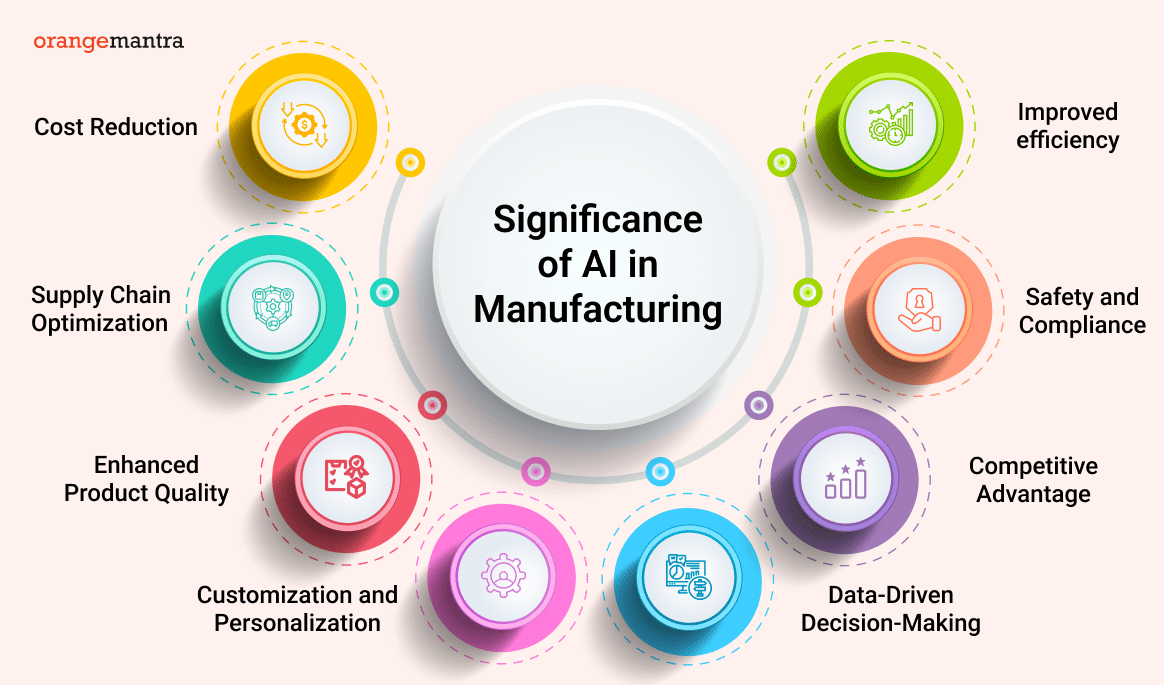
Source: https://www.orangemantra.com/blog/ai-in-manufacturing-industry/
The future of using AI in manufacturing holds even greater possibilities, with new trends and technologies set to transform the industry further. AI will not just automate processes; it will redefine how factories operate, making them smarter, more sustainable, and more efficient than ever.
1. Generative AI for Design and Prototyping
Generative AI, which uses algorithms to create designs, is revolutionizing product development. Engineers can input specific requirements—like material constraints or performance goals—and let AI generate multiple design options. This speeds up prototyping and ensures optimal designs. For example, General Motors used generative AI to redesign lightweight components for vehicles, reducing material usage. This technology shortens design cycles and drives innovation in creating more efficient products.
2. Greater Use of Digital Twins
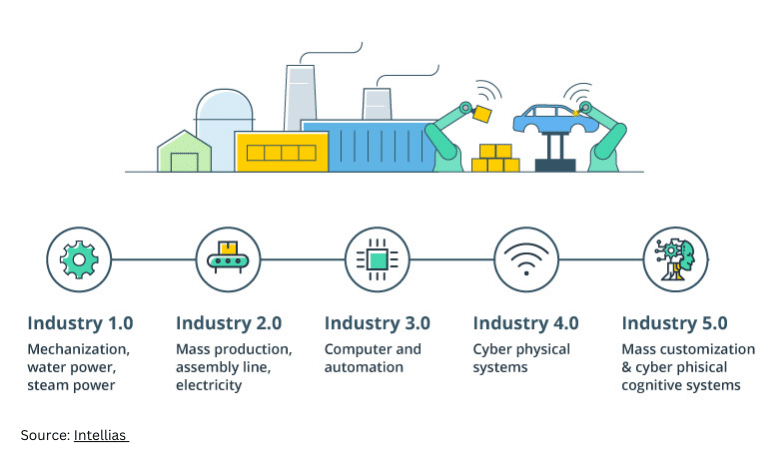
Source: https://www.titanteal.com/unraveling-the-future-with-digital-twin-Industry-4-0-and-5-0
Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical systems—are becoming a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. AI-powered digital twins allow manufacturers to monitor real-time performance, run simulations, and predict outcomes without disrupting actual operations. Manufacturers plan to adopt digital twins by 2026 to enhance production AI efficiency and reduce costs. These virtual models also help in predictive maintenance, ensuring machines run smoothly while minimizing downtime.
3. AI-Driven Sustainability Initiatives
Source: https://nextbillion.net/cutting-edge-agriculture-artificial-intelligence/
Sustainability is a pressing concern, and AI is emerging as a powerful tool to address it. AI systems can analyze energy consumption, optimize resource use, and suggest ways to reduce waste and emissions. For instance, in 2024, Siemens used AI to cut carbon emissions in its factories by 15% through energy optimization.
AI can also help manufacturers track their carbon footprint and implement eco-friendly practices, aligning with global sustainability goals.
4. Predictions for AI’s Impact on Industry 4.0 and Beyond
AI is the backbone of Industry 4.0, driving the shift toward fully automated and interconnected smart factories. AI will become even more integrated with other technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and 5G in the coming years. AI is expected to boost manufacturing productivity. Factories will use AI not just for efficiency but also for personalization, enabling mass customization of products at scale.
Conclusion
Experts agree that using AI in manufacturing is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s the driving force behind smarter, more efficient factories today. According to industry leaders, manufacturers who invest in AI are better positioned to compete in a fast-changing global market. With AI powering everything from predictive maintenance to supply chain optimization, it’s clear that this technology is not just an add-on but a necessity for long-term success.
However, implementing AI effectively requires more than just tools—it demands expertise. Collaborating with skilled professionals ensures that solutions are tailored to your factory AI unique needs. From designing AI-powered systems to integrating them with existing processes, the right team can help unlock the full potential of AI in manufacturing.
SHARE THIS POST